Briefly
- OpenAI’s GDPval benchmark examined actual jobs—authorized briefs, code, experiences—and located AI matching human consultants at breakneck velocity.
- Claude and GPT-5 outperformed seasoned professionals in 44 occupations, enhancing threefold in simply over a yr.
- The research confirmed the primary wave of disruption will hit office-based jobs, from coders to legal professionals and journalists.
OpenAI unveiled GDPval on Thursday—a benchmark that tries to evaluate qualitatively whether or not AI can do your precise job.
These usually are not hypothetical examination questions, however actual deliverables: authorized briefs, engineering blueprints, nursing care plans, monetary experiences—the type of work, that’s, that pays mortgages. The researchers intentionally centered on occupations the place at the very least 60% of duties are computer-based—roles they describe as “predominantly digital.”
That scope covers skilled companies akin to software program builders, legal professionals, accountants, and challenge managers; finance and insurance coverage positions like analysts and customer support reps; and information-sector jobs starting from journalists and editors to producers and AV technicians. Healthcare administration, white-collar manufacturing roles, and gross sales or actual property managers additionally characteristic prominently.
Inside that set, the work most uncovered to AI overlaps with the sorts of digital, knowledge-intensive actions that enormous language fashions already deal with nicely:
- Software program improvement, which represents the biggest wage pool within the dataset, stands out as particularly susceptible.
- Authorized and accounting work, with its heavy reliance on paperwork and structured reasoning, can be excessive on the listing, as are monetary analysts and customer support representatives.
- Content material manufacturing roles—editors, journalists, and different media employees—face comparable pressures given AI’s rising fluency in language and multimedia technology.
The absence of guide and bodily labor jobs within the research highlights its boundaries: GDPval was not designed to measure publicity in fields like building, upkeep, or agriculture. As a substitute, it underscores the purpose that the primary wave of disruption is more likely to strike white-collar, office-based jobs—the very sorts of labor as soon as assumed to be most insulated from automation.
The report builds on a two-year-old OpenAI/College of Pennsylvania research that claimed that as much as 80% of U.S. employees may see at the very least 10% of their duties affected by LLMs, and round 19% of employees may see at the very least 50% of their duties affected. Probably the most imperiled (or reworked) jobs are white-collar, knowledge-heavy ones—particularly in legislation, writing, evaluation, and buyer interplay.
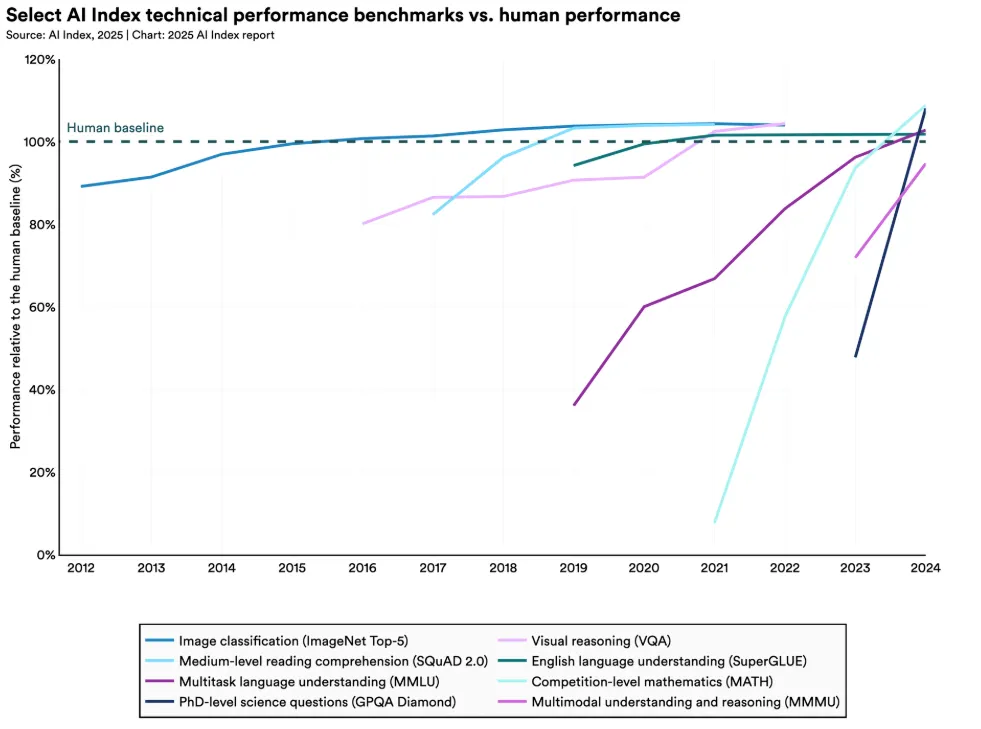
However the unsettling half is not at this time’s numbers. It is the trajectory. At this tempo, the statistics counsel that AI may match human consultants throughout the board by 2027. That is actually near AGI requirements, and will imply that even duties thought-about unsafe or too specialised for automation might quickly turn out to be accessible to machines, threatening fast office transformations.
OpenAI examined 1,320 duties throughout 44 occupations—not random jobs, however roles within the 9 sectors that drive most of America’s GDP. Software program builders, legal professionals, nurses, monetary analysts, journalists, engineers: the individuals who thought their levels would shield them from automation.
Every process got here from professionals with a mean of 14 years of expertise—not interns or current grads, however seasoned consultants who know their craft. The duties weren’t easy both, averaging seven hours of labor with some stretched to a number of weeks of effort.
In keeping with OpenAI, the fashions accomplished these duties as much as 100 occasions quicker and considerably cheaper than people in some API-specific duties—which is to be anticipated and has been the case for many years. On extra specialised duties, the development was slower, however nonetheless noticeable.
Even accounting for evaluate time and the occasional do-over when the AI hallucinated one thing weird, the economics tilt exhausting towards automation.
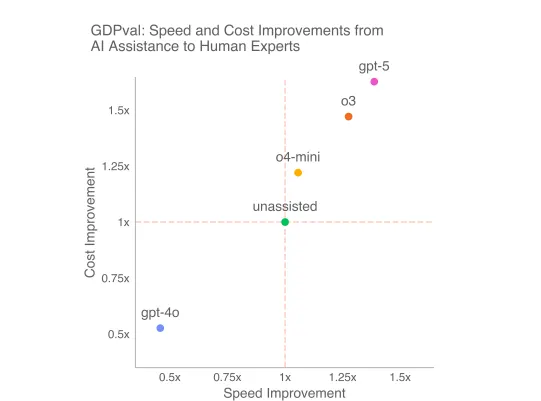
However cheer up: Simply because a job is uncovered doesn’t imply it disappears. It could be augmented (as an illustration, legal professionals and journalists utilizing LLMs to write down quicker) moderately than get replaced.
And so far as AI has gone, hallucinations are nonetheless a ache for companies. The analysis exhibits AI failing most frequently on instruction-following—35% of GPT-5’s losses got here from not totally greedy what was requested. Formatting errors plagued one other 40% of failures.
The fashions additionally struggled with collaboration, shopper interplay, and something requiring real accountability, which OpenAI ignored of the research. No one’s suing an AI for malpractice but. However for solo digital deliverables—the experiences, shows, and analyses that fill most information employees’ days—the hole is closing quick.
OpenAI admits that GDPval at this time covers a really restricted variety of duties folks do of their actual jobs. The benchmark cannot measure interpersonal expertise, bodily presence, or the thousand micro-decisions that make somebody priceless past their deliverables.
Nonetheless, when funding banks begin evaluating AI-generated competitor analyses to these from human analysts, when hospitals consider AI nursing care plans towards these from skilled nurses, and when legislation companies take a look at AI briefs towards affiliate work—that is not hypothesis anymore. That is measurement.
Typically Clever E-newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI mannequin.
