Briefly
- Yale and Brookings researchers discovered no proof of mass AI-driven unemployment 33 months after ChatGPT’s launch.
- Occupational shifts rose about one share level above early 2000s ranges, however matched typical tech transitions.
- Excessive AI-exposure jobs—legislation, finance, customer support—confirmed no displacement in federal knowledge.
Three years after ChatGPT burst onto the scene, American employees are nonetheless displaying as much as their jobs. A brand new examine from Yale College’s Price range Lab and the Brookings Establishment examined federal employment knowledge by July, and located that AI has but to set off the mass unemployment that know-how executives have been predicting.
The researchers tracked how rapidly the combination of occupations has modified since November 2022, when OpenAI launched ChatGPT to the general public. Whereas jobs are shifting barely sooner than lately—about one share level increased than throughout the early 2000s web growth—the modifications look like fairly typical for technological transitions slightly than the financial upheaval many feared.
Winter should still be coming—simply not proper now.
“We aren’t in an economy-wide jobs apocalypse proper now; it is principally steady,” Molly Kinder, a senior fellow at Brookings and co-author of the paper, advised The Monetary Instances. “That must be a reassuring message to an anxious public.”
The hole between Silicon Valley rhetoric and office actuality has grown stark. As reported by Decrypt, Anthropic CEO Dario Amode mentioned that as much as 50% of entry-level white-collar roles might disappear inside 5 years, whereas Geoffrey Hinton—often known as the “Godfather of AI”—estimated that AI might dramatically worsen the monetary hole if issues hold going the best way they’re.
“What’s really going to occur is wealthy persons are going to make use of AI to interchange employees,” he advised the Monetary Instances. “It’s going to create huge unemployment and an enormous rise in income. It’s going to make just a few folks a lot richer and most of the people poorer. That’s not AI’s fault, that’s the capitalist system.”
OpenAI’s Sam Altman has repeatedly singled out customer support jobs as significantly weak, with a latest examine arguing that AI matched expert human employees in at the very least 44 enterprise areas.
However knowledge tells a special story. Yale researchers examined a number of metrics, together with occupational combine modifications, industry-specific shifts, and AI publicity ranges throughout completely different job classes. Employees in occupations theoretically most uncovered to AI automation, based mostly on OpenAI’s personal metrics, confirmed no indicators of displacement. About 18% of employees maintain jobs within the highest AI-exposure class, a proportion that has remained flat since January 2023.
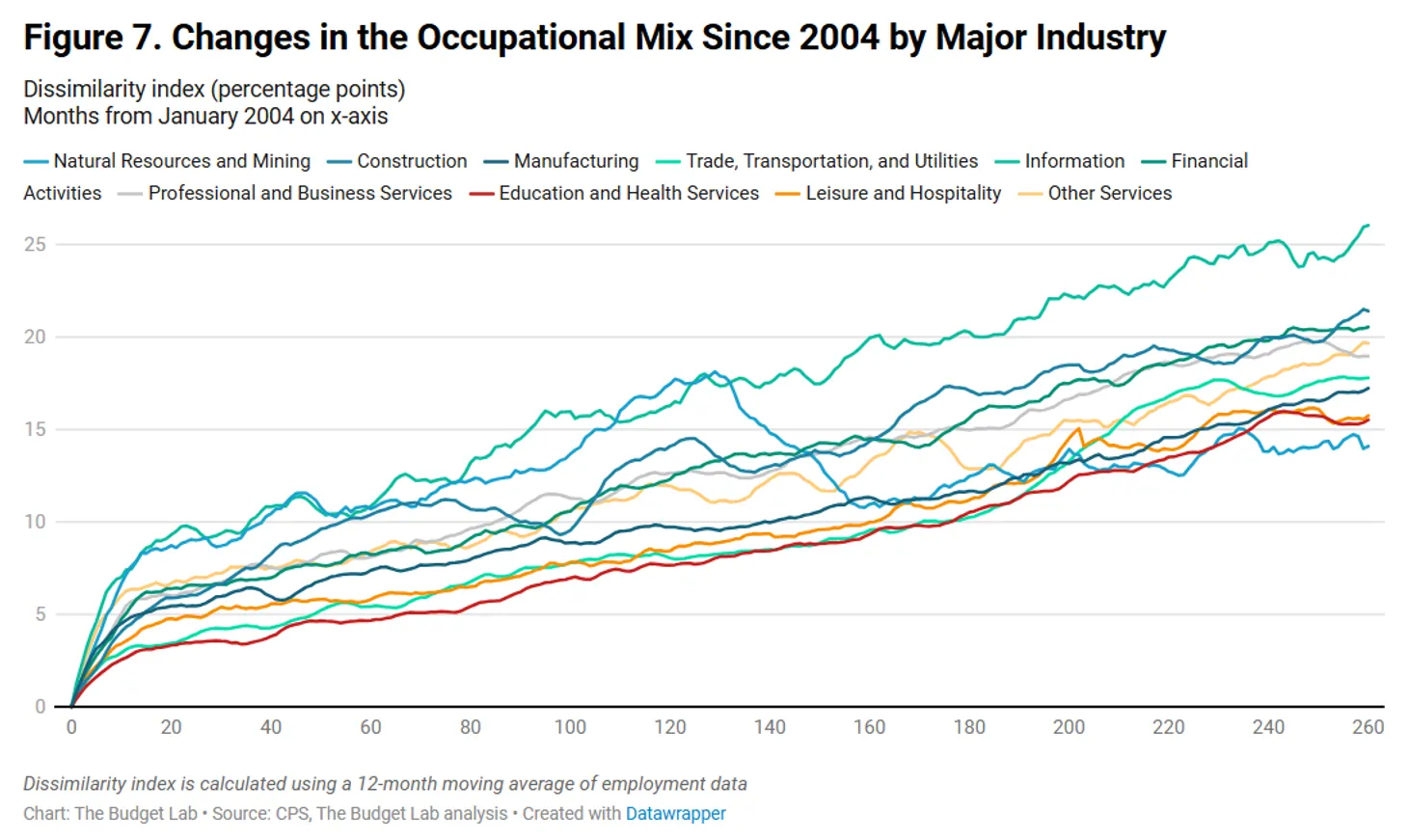
The knowledge sector, which incorporates newspapers, films, and knowledge processing, confirmed the biggest occupational shifts. However these modifications started earlier than ChatGPT’s launch, suggesting industry-specific components slightly than AI disruption. Finance {and professional} companies displayed comparable patterns—actions that predated the supposed AI revolution.
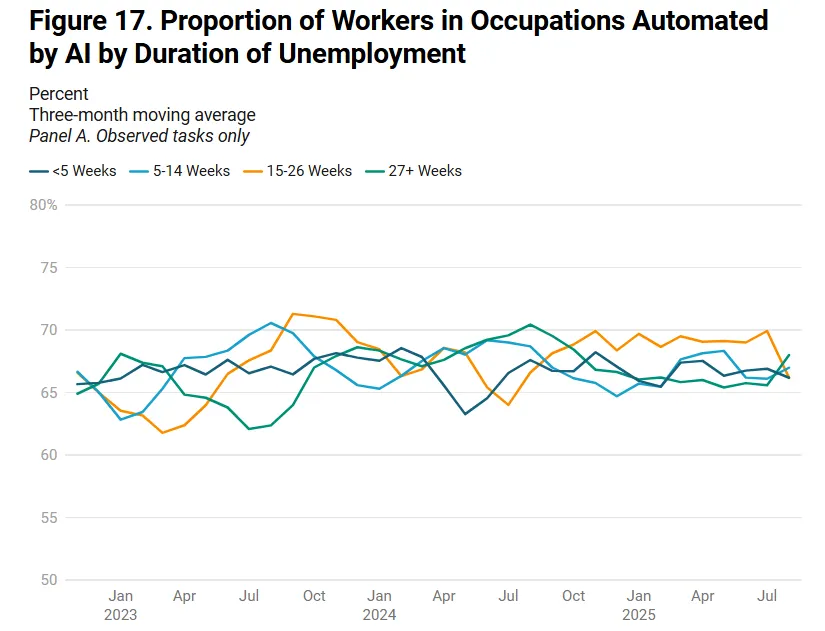
Younger school graduates have struggled, with unemployment amongst 20- to 24-year-olds with bachelor’s levels rising to 9.3% in August from 4.4% in April. However the analysis group discovered the sample matched that of older diploma holders aged 25 to 29, indicating a broader labor market slowdown slightly than AI alternative. The dissimilarity between these age teams has fluctuated inside a slim 30-33 % vary since 2021, displaying no acceleration after ChatGPT’s arrival.
Historic precedent helps the researchers’ skepticism about speedy disruption. Computer systems did not turn into normal workplace tools till almost a decade after their public launch. The web’s office transformation stretched out even longer. The examine notes that occupational change peaked throughout the Nineteen Forties and Fifties—durations of huge industrial shifts—at charges of 20-21%. Present modifications hover round 10%.
“Traditionally, widespread technological disruption in workplaces tends to happen over a long time, slightly than months or years,” the researchers wrote.
The researchers acknowledged vital knowledge limitations. OpenAI’s “publicity” metrics measure theoretical vulnerability slightly than precise AI utilization. Anthropic’s utilization knowledge from its Claude chatbot exhibits heavy focus amongst coders and writers—not consultant of broader workforce patterns. The group referred to as for complete utilization knowledge from all main AI firms to correctly assess office impacts.
The analysis group plans month-to-month updates to trace any rising patterns. For now, almost three years into the AI revolution, probably the most dramatic office change seems to be how a lot executives speak about AI slightly than what it is really doing to employment on a broad scale.
Usually Clever E-newsletter
A weekly AI journey narrated by Gen, a generative AI mannequin.
